Home page for the EDELWEISS-III experiment
The Edelweiss experiment is dedicated to the direct detection of dark matter particles with bolometric detectors located at the underground laboratory of Modane (the LSM). The results of the stage II of this experiment are published, while the third phase is in scientific exploitation. On this Web site you will find the following sections:
- Some presentations of the experiment, from a wide-audience introduction to a more technical documentation.
- A list of our financing institutions as well as of the collaboration members and the staff in contact with the collaboration.
- All our publications: refereed articles, conference proceedings, theses...
- Some links.
 |
 |
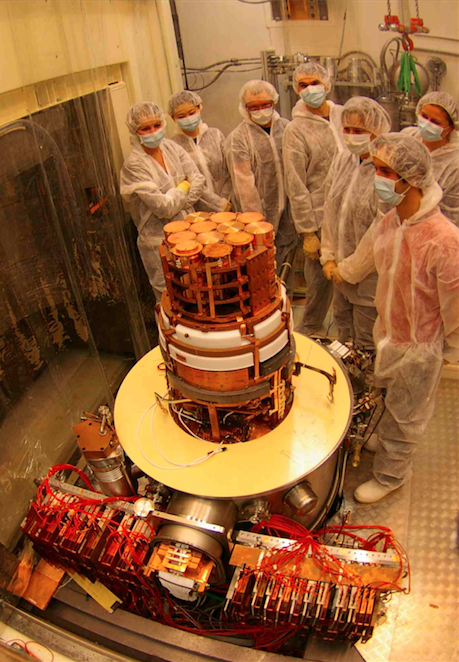 |
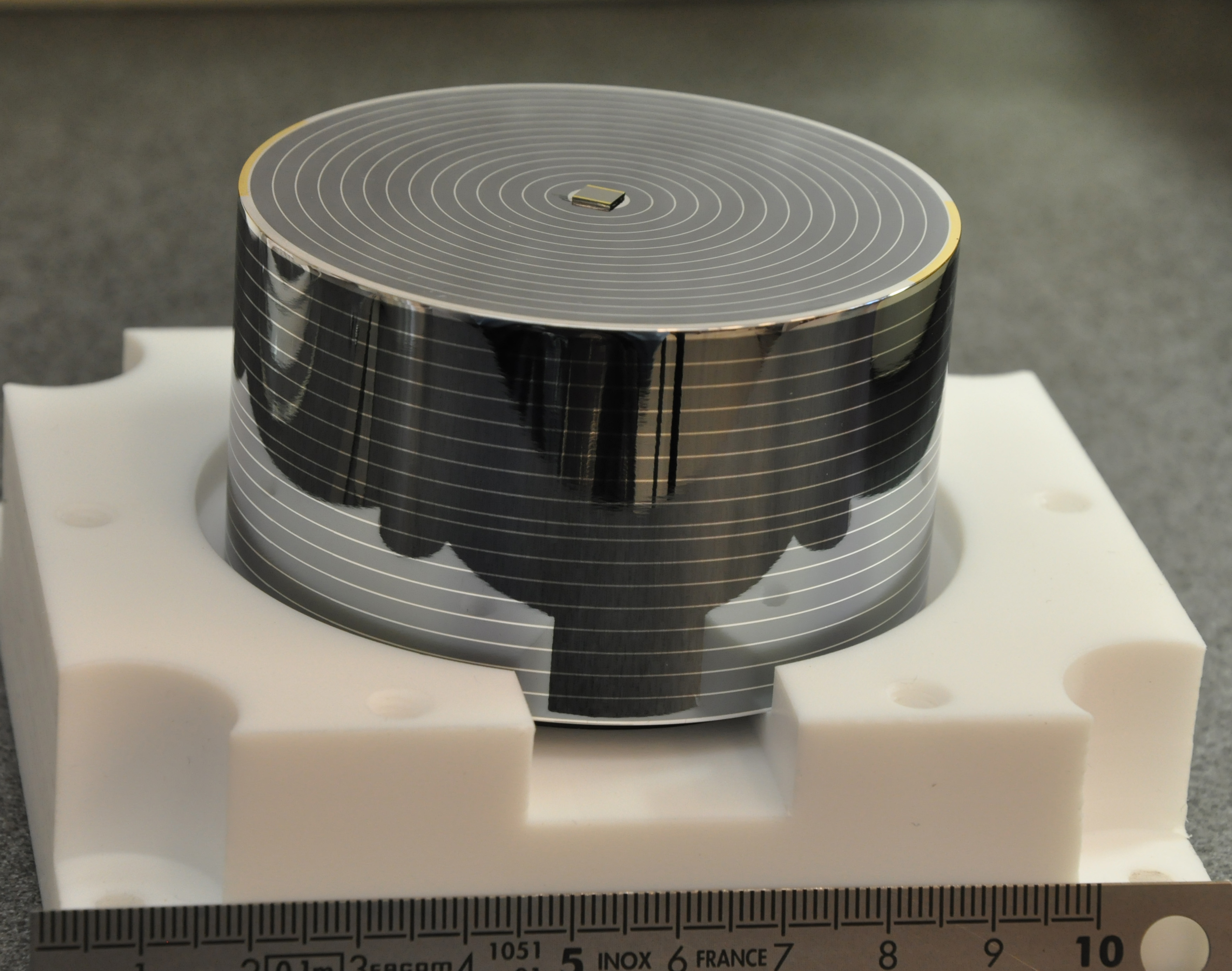
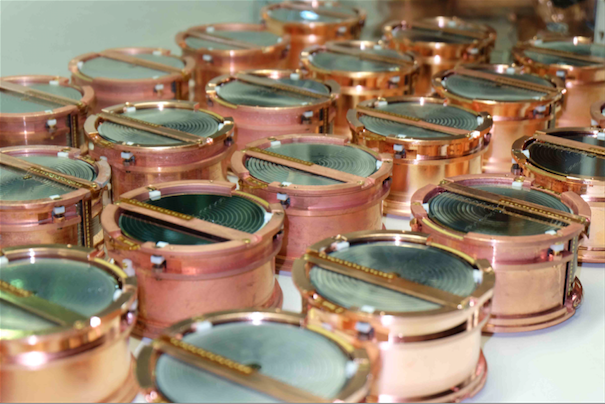
| "FID" Full InterDigit germanium bolometer | The FID bolometers ready at Modane | Final installation of the EDELWEISS-III setup |
 |
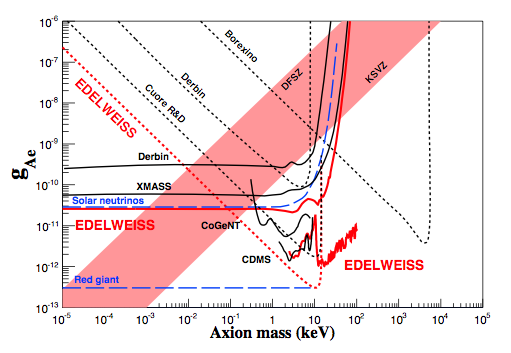 |
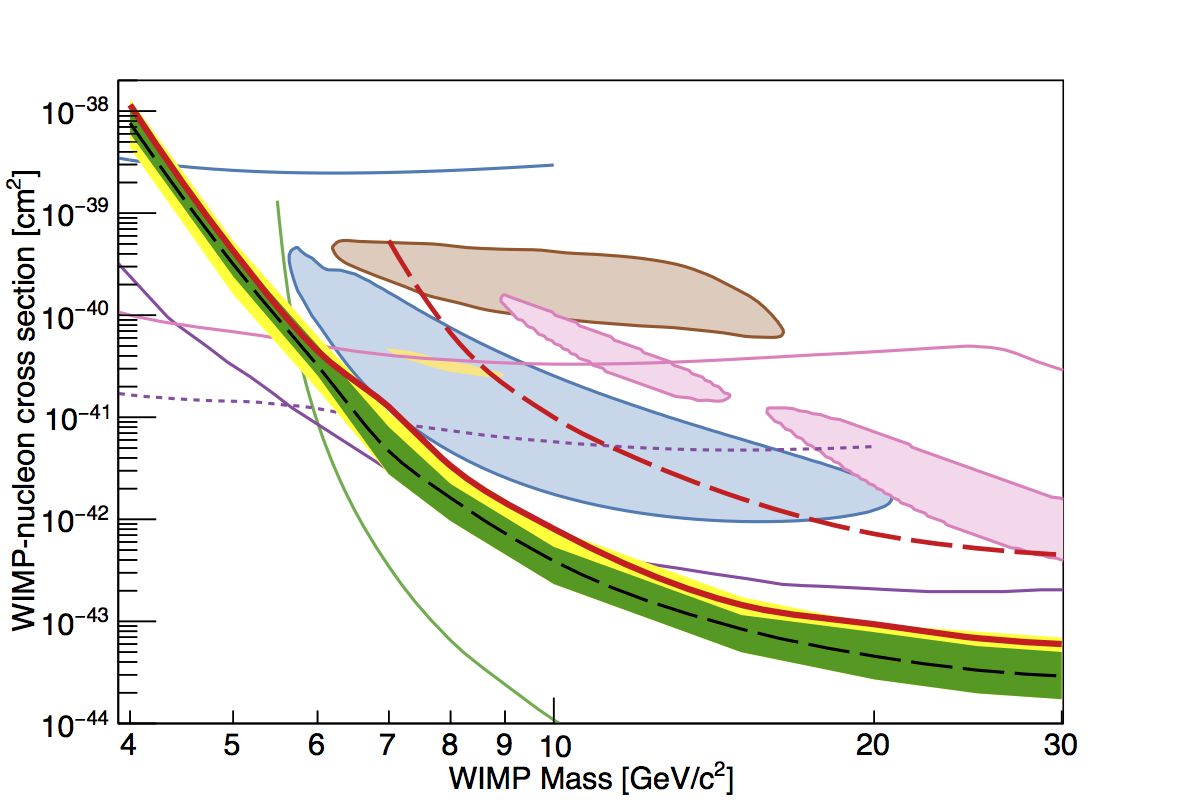
| Limit on low-mass WIMPs with EDELWEISS-III, JCAP05 (2016) 019 | Limits on the axion coupling to electrons (EDELWEISS-II data) |
Summer 2016 - New scientific results from the long EDELWEISS-III physics run
A set of new results were derived from the 2014-2015 EDELWEISS-III physics run, and submitted to journals for publication.- Thanks to the electrode design of our detectors, the signals induced by charge-carrier trapping could be studied in depth with analytical models and used to improve several aspects of our data analysis.
- The low-energy performance of FID detectors, combined with the long background exposure achieved, permitted to measure several cosmogenic activations in germanium, derive production rates and compare them with theoretical modelling. For the first time we could unambiguously measure the tritium beta spectrum inside germanium - a key background for future germanium-based dark matter searches.
- An improved search for low-mass WIMPs was carried out, using our full knowledge of the relevant backgrounds to extract the WIMP signals with a likelihood method. These results improve significantly our sensitivity for WIMP masses below 10 GeV.
September 2015 - Preliminary results from a long EDELWEISS-III physics run
A long physics run ("Run 308") took place between Summer 2014 and Spring 2015. Preliminary results from a search for low-mass WIMPs were presented at the TAUP conference, using data taken during this run by 8 detectors. The derived limit on the WIMP-nucleon cross-section represents roughly an order-of-magnitude improvment with respect to EDELWEISS-II, for WIMP masses in the 5 to 30 GeV range. It now excludes completely all previous "low-mass WIMP" claims, which confirms results by the SuperCDMS experiment. A publication is in preparation, while further R&D is ongoing to drastically improve the detector sensitivity down to GeV WIMP masses.Update Spring 2016 : the final result is published in JCAP05 (2016) 019 [arxiv:1603.05120]
Summer 2013 - Axion searches with the EDELWEISS-II experiment (arxiv:1307.1815)
For the first time, the EDELWEISS experiment presents new constraints on the coupling of axions or "ALP" particles. While EDELWEISS is primarily designed to search for WIMP-induced nuclear recoils, it is also sensitive to axion-induced electron recoils, thanks to its high-exposure, low background and good energy resolution. In this publication we used EDELWEISS-II data to place bounds on axion couplings using four different search channels. The main results are :- Each of these searches provides a constraint on a given axion coupling or combination of couplings: axion-photon, axion-electron or effective axion-nucleus coupling. For example, we set a 95% CL limit on the coupling to photons <2.13x10^-9 GeV^-1 in a mass range not fully covered by axion helioscopes. We also constrain the coupling to electrons < 2.56x10^-11, similar to the more indirect solar neutrino bound.
- When combining these bounds, we are able to fully exclude the mass range 0.91eV < m < 80keV for the so-called DFSZ axion model, and 5.77eV < m < 40keV for the KSVZ model.
 Edelweiss
Edelweiss